Consortium
UNIBAS, the SAFE coordinator has been working with several technologies (e.g., adsorption, ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis, heterogeneous/homogeneous photo-catalysis, various nanostructured materials of modified natural origin) applied in NANOWATT for chemical and microbial contaminants. SAFE novelty will be the highly efficient exploitation of nanostructured clay micelles and clay-vesicle-based filtration materials and new photocatalytic processes (TiO2 immobilized on glass and/or peroxymonosulphate). SCIWARE will bring into SAFE its innovations for the efficient supply of water from unusual sources and the collaboration with several stakeholders (e.g., small communities, artisans, families, farmers, agro-food businesses, and small entrepreneurs) and, through Belowground, the root symbiosis in induced defence in crops, like tomatoes. IRSA will provide WANT-BIO experience on both anaerobic and aerobic processes towards an onsite cost-efficient integrated anaerobic-aerobic system to support the rural societies and industries in producing cleaner wastewater (maximizing environmental protection, and reducing energy, manpower and maintenance requirements with low complexity treatment units). IRSA will also take advantage of SWaRM-Net experience of monitoring, efficient use of water resources, water bodies management, enhancement of the thermal properties of water network, recovery of energy and products through wastewater treatment, as well as extreme events and odour emissions risk management. UM will link IDOUM to SAFE regarding energy-efficient, cost-effective, and robust decentralized domestic wastewater treatment systems (constructed wetlands and low-cost heterogeneous Fenton treatment). CERTE will implement INWAT diagnosis methodologies for emergent pollutants from wastewater release on intermittent rivers, as well as the optimization of their analysis protocols. ICRA will transfer its competences about circular economy, water reuse in a touristic city and greywater treatment with NBS and other technologies, also addressing organic micropollutants (from CLEaN-TOUR), and demonstration of water loops with innovative regenerative business models for the Mediterranean region (from HYDROUSA). Morocco will use MASSIRE integrating multiple water sources and local institutions for enhanced food security in north Africa’s hinterland by reinforcing agricultural and rural innovation systems. And finally, SAPIENZA will apply in SAFE optimization tools from ExCornSeed (Horizon2020), modelling and cost/benefit analysis (both on an economical and environmental point of view).
Working Packages
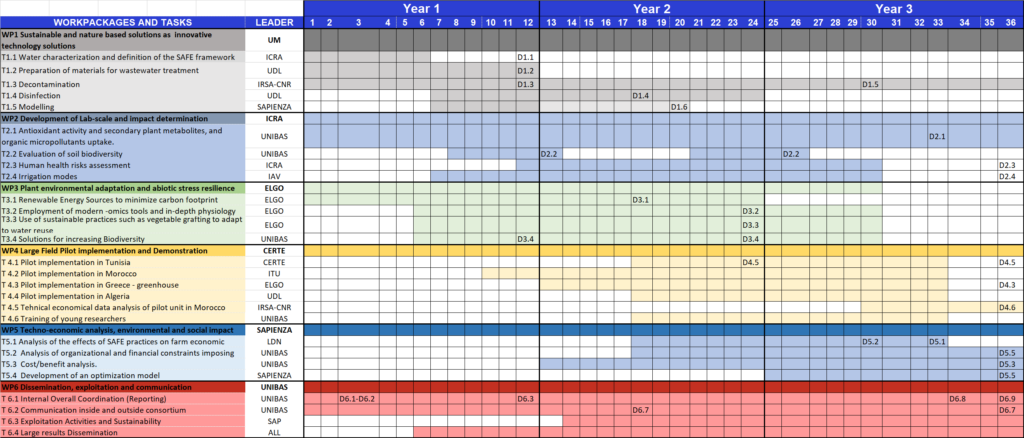
Work Planning
Latest news
Here you can find our news
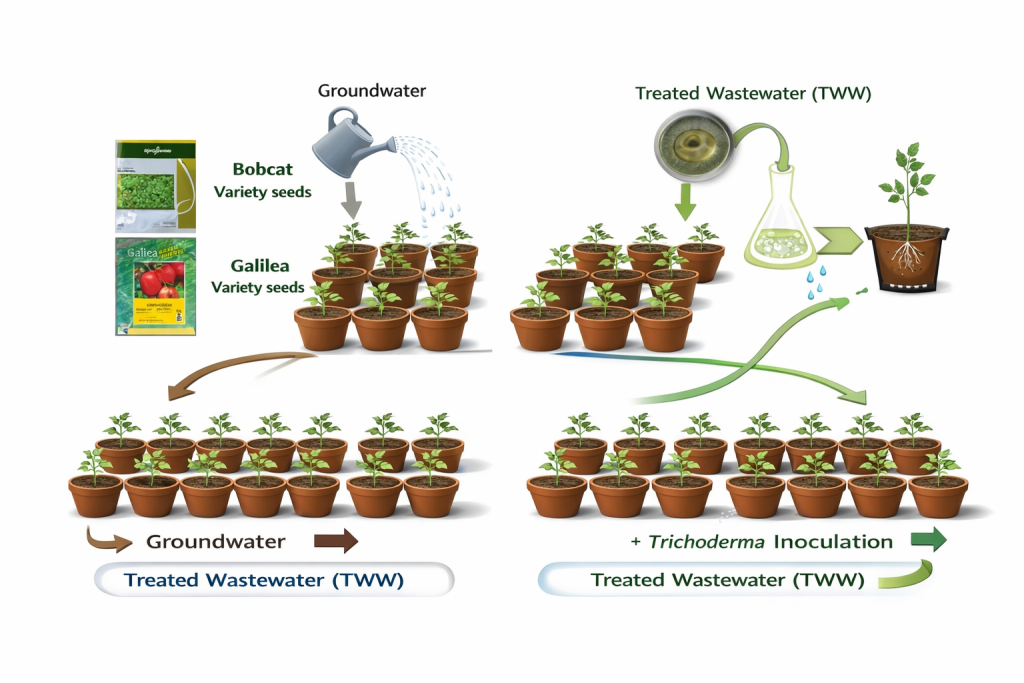
PRIMA-SAFE study highlights: treated wastewater plus Trichoderma boosts tomato growth and yield under greenhouse conditions
Why this work matters for PRIMA-SAFE Water scarcity is pushing Mediterranean and semi-arid regions to…
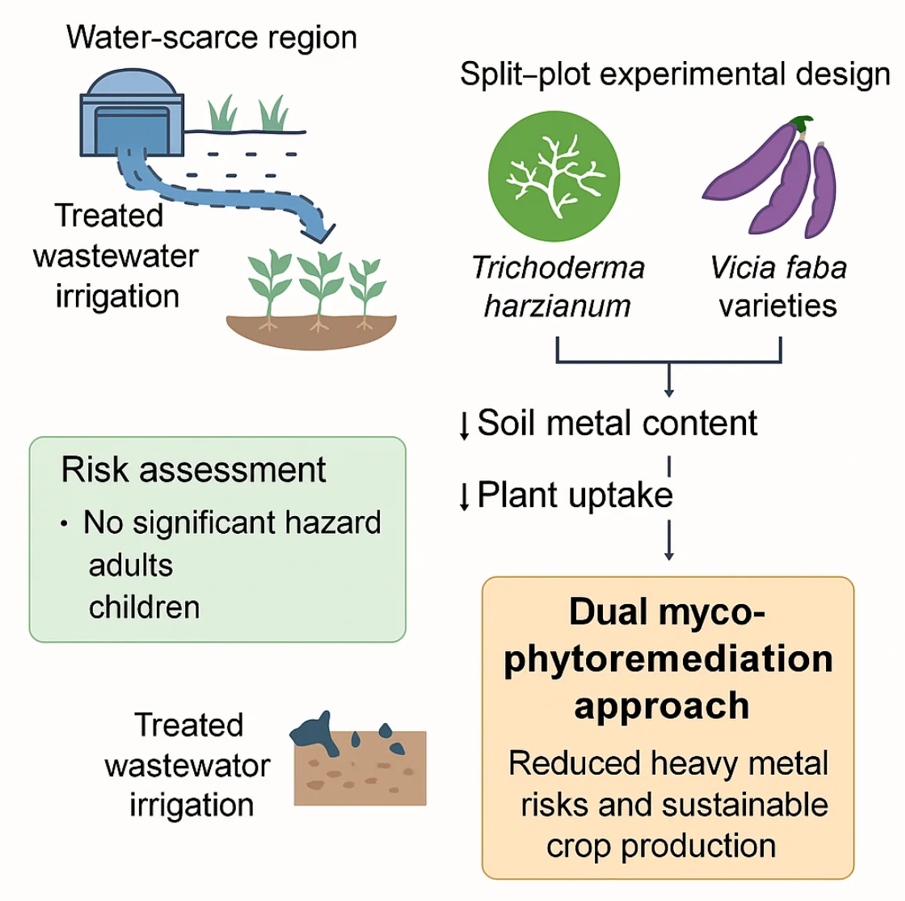
PRIMA-SAFE publication: a fungi–crop strategy to reduce heavy-metal risks under wastewater irrigation
What this new paper is about PRIMA-SAFE has a new open-access publication that addresses a…
PRIMA-SAFE at the Second Pan African University International Conference: Advancing Sustainable Water Treatment
Emerging contaminants in water systems pose a growing threat to environmental integrity, public health, and…
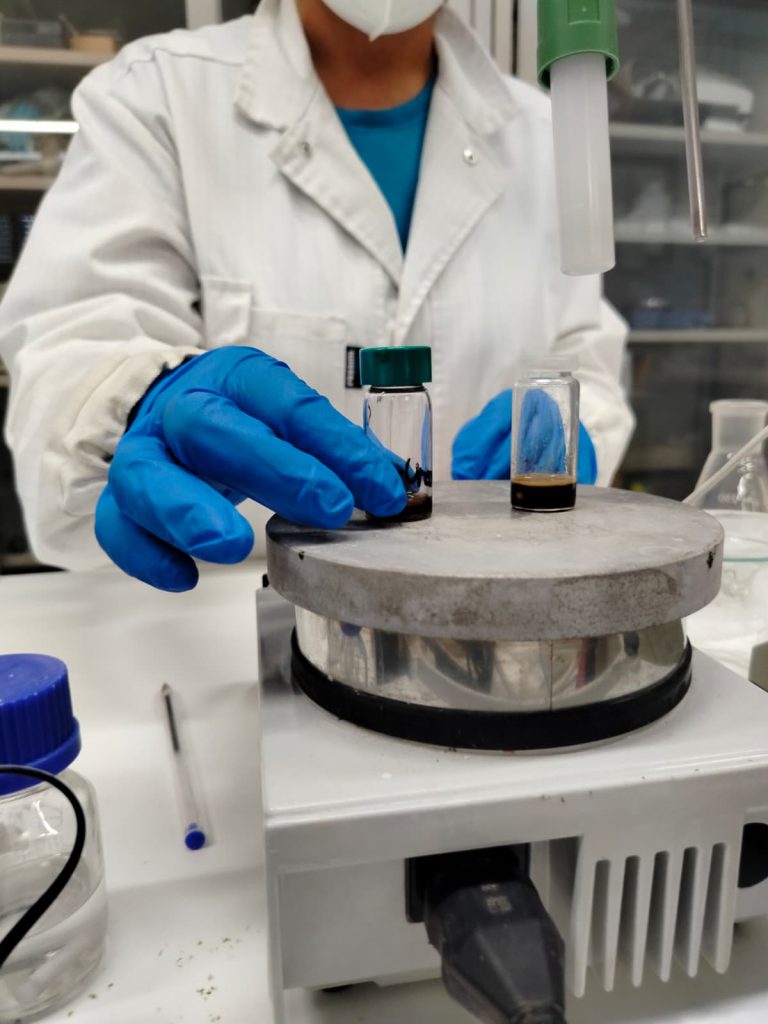
Inside the PRIMA-SAFE Lab: How We Analyze Water for Safe Reuse
From field samples to risk-based decisions: PRIMA-SAFE labs analyze reclaimed water to track pharmaceuticals, antibiotic…
Open Access Publication Highlights Biochar-Based Adsorption for Scalable Water Treatment
As part of the research developed under the PRIMA-SAFE project, a new peer-reviewed article has…
SAFE at ecoSTP2025: Presenting Sustainable Water Treatment Solutions in Stockholm
From June 23rd to 26th, 2025, the SAFE project was proudly represented at the 7th…